想法很好的一个包,但是稳定性太差,bug多,不推荐,有这点闲工夫,一个回归都跑完了。
OneR
Holger von Jouanne-Diedrich (2017), Holte (1993) 使用单变量分析,类似于WOE等,但是构建方式不同,关键是不用手动切分WOE,可以自动切好,非常方便。
The following story is one of the most often told in the Data Science community: some time ago the military built a system which aim it was to distinguish military vehicles from civilian ones. They chose a neural network approach and trained the system with pictures of tanks, humvees and missile launchers on the one hand and normal cars, pickups and trucks on the other. After having reached a satisfactory accuracy they brought the system into the field (quite literally). It failed completely, performing no better than a coin toss. What had happened? No one knew, so they re-engineered the black box (no small feat in itself) and found that most of the military pics where taken at dusk or dawn and most civilian pics under brighter weather conditions. The neural net had learned the difference between light and dark! (Holger von Jouanne-Diedrich 2017, @Holte1993)
实际上swallow learning、deep learning、复杂模型、简单模型都有一个平衡。 我们需要区分: 简单模型找出我们我们足够知道的信息,复杂模型去负责特别的复杂的信息方面。
例子1
library(OneR)data <- optbin(iris)
model <- OneR(data, verbose = TRUE)##
## Attribute Accuracy
## 1 * Petal.Width 96%
## 2 Petal.Length 95.33%
## 3 Sepal.Length 74.67%
## 4 Sepal.Width 55.33%
## ---
## Chosen attribute due to accuracy
## and ties method (if applicable): '*'summary(model)##
## Call:
## OneR.data.frame(x = data, verbose = TRUE)
##
## Rules:
## If Petal.Width = (0.0976,0.791] then Species = setosa
## If Petal.Width = (0.791,1.63] then Species = versicolor
## If Petal.Width = (1.63,2.5] then Species = virginica
##
## Accuracy:
## 144 of 150 instances classified correctly (96%)
##
## Contingency table:
## Petal.Width
## Species (0.0976,0.791] (0.791,1.63] (1.63,2.5] Sum
## setosa * 50 0 0 50
## versicolor 0 * 48 2 50
## virginica 0 4 * 46 50
## Sum 50 52 48 150
## ---
## Maximum in each column: '*'
##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test:
## X-squared = 266.35, df = 4, p-value < 2.2e-16plot(model)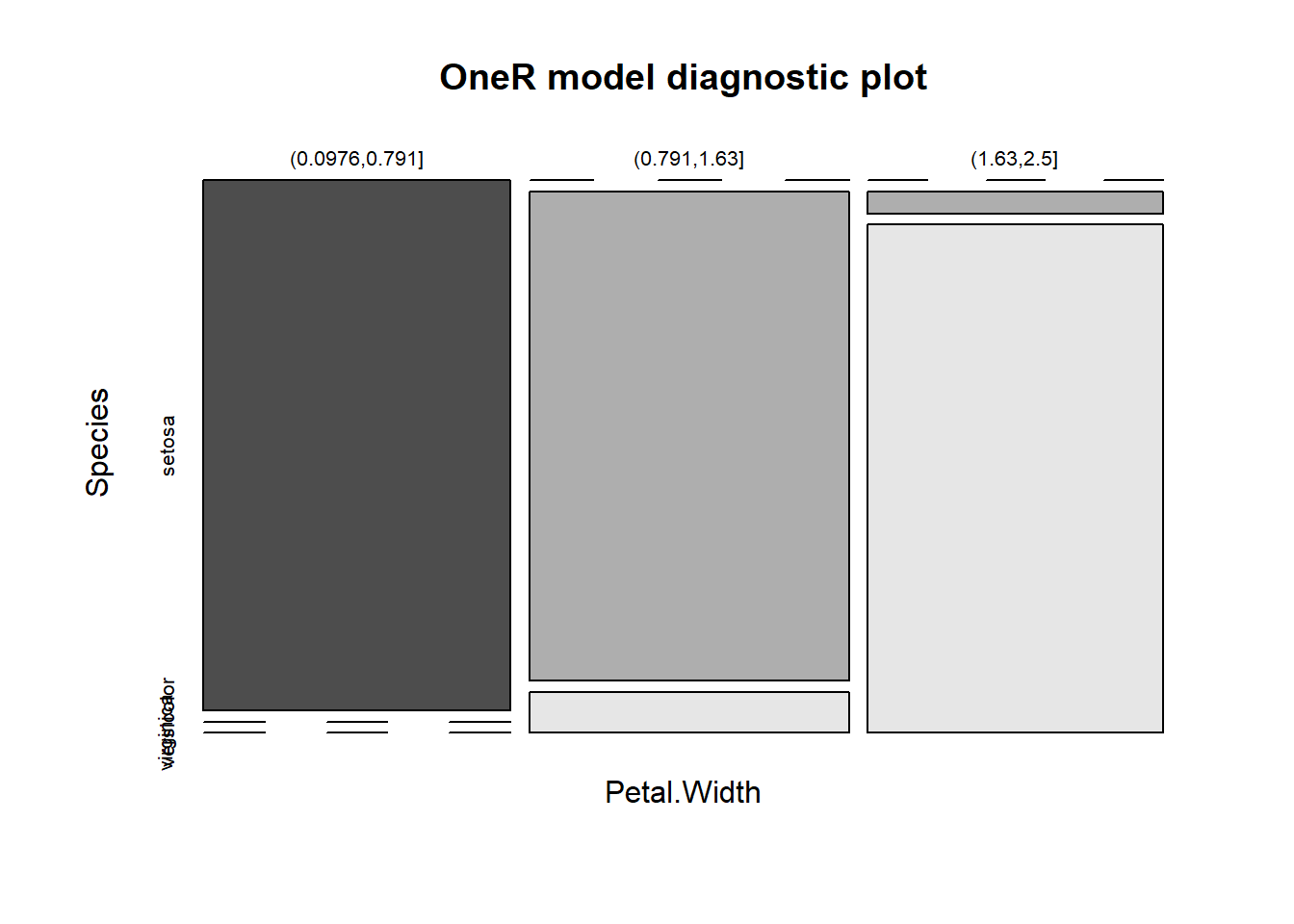
prediction <- predict(model, data)
eval_model(prediction, data)##
## Confusion matrix (absolute):
## Actual
## Prediction setosa versicolor virginica Sum
## setosa 50 0 0 50
## versicolor 0 48 4 52
## virginica 0 2 46 48
## Sum 50 50 50 150
##
## Confusion matrix (relative):
## Actual
## Prediction setosa versicolor virginica Sum
## setosa 0.33 0.00 0.00 0.33
## versicolor 0.00 0.32 0.03 0.35
## virginica 0.00 0.01 0.31 0.32
## Sum 0.33 0.33 0.33 1.00
##
## Accuracy:
## 0.96 (144/150)
##
## Error rate:
## 0.04 (6/150)
##
## Error rate reduction (vs. base rate):
## 0.94 (p-value < 2.2e-16)optbin直接切分好了data的各个连续变量。
这是这个包的一次分析全部使用的函数,非常简单。
例子2
data(breastcancer)
data <- breastcancer
set.seed(12)
random <- sample(1:nrow(data), 0.8 * nrow(data))
data_train <- optbin(data[random, ], method = "infogain")
data_test <- data[-random, ]
model_train <- OneR(data_train, verbose = TRUE)##
## Attribute Accuracy
## 1 * Uniformity of Cell Size 92.87%
## 2 Uniformity of Cell Shape 91.59%
## 3 Bare Nuclei 91.22%
## 4 Bland Chromatin 90.68%
## 5 Single Epithelial Cell Size 90.49%
## 6 Normal Nucleoli 89.4%
## 7 Marginal Adhesion 87.57%
## 8 Clump Thickness 85.37%
## 9 Mitoses 79.34%
## ---
## Chosen attribute due to accuracy
## and ties method (if applicable): '*'summary(model_train)##
## Call:
## OneR.data.frame(x = data_train, verbose = TRUE)
##
## Rules:
## If Uniformity of Cell Size = (0.991,2] then Class = benign
## If Uniformity of Cell Size = (2,10] then Class = malignant
##
## Accuracy:
## 508 of 547 instances classified correctly (92.87%)
##
## Contingency table:
## Uniformity of Cell Size
## Class (0.991,2] (2,10] Sum
## benign * 324 30 354
## malignant 9 * 184 193
## Sum 333 214 547
## ---
## Maximum in each column: '*'
##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test:
## X-squared = 392.05, df = 1, p-value < 2.2e-16plot(model_train)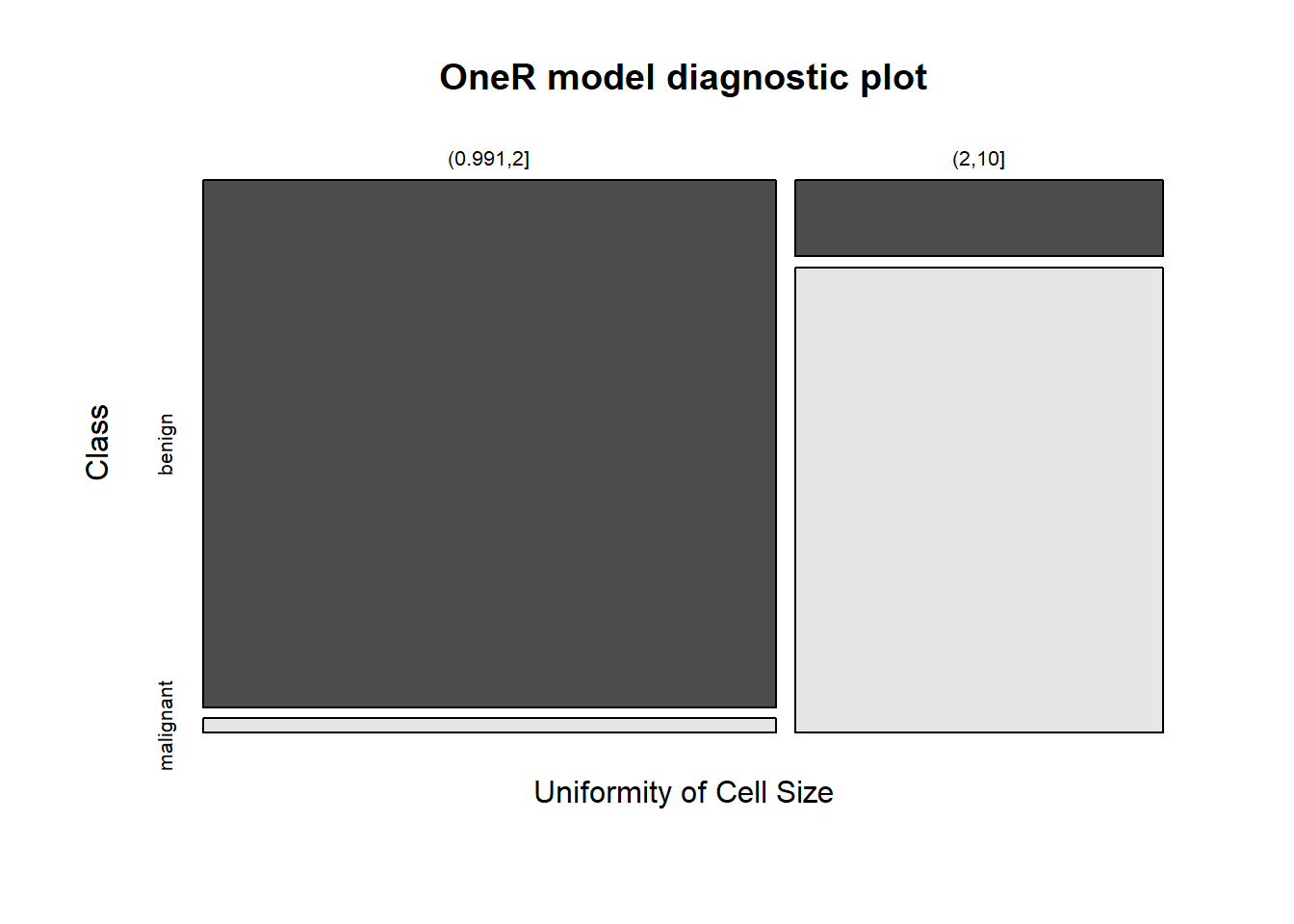
prediction <- predict(model_train, data_test)
eval_model(prediction, data_test)##
## Confusion matrix (absolute):
## Actual
## Prediction benign malignant Sum
## benign 83 3 86
## malignant 10 44 54
## Sum 93 47 140
##
## Confusion matrix (relative):
## Actual
## Prediction benign malignant Sum
## benign 0.59 0.02 0.61
## malignant 0.07 0.31 0.39
## Sum 0.66 0.34 1.00
##
## Accuracy:
## 0.9071 (127/140)
##
## Error rate:
## 0.0929 (13/140)
##
## Error rate reduction (vs. base rate):
## 0.7234 (p-value = 1.69e-11)infogain类似于决策树。
函数解释
OneR主要的学习函数。bin()等距分bin,参数nbins、labelsoptbin自动分binmaxlavels剔除levels太多的分类变量eval_model类似于summary
data_frame(numeric = c(1:26), alphabet = letters) %>%
maxlevels() %>%
datatable()报错
使用前数据一定要as.data.frame。
并且禁不起大数据考验。
这个包很水。
参考文献
Holger von Jouanne-Diedrich. 2017. OneR: One Rule Machine Learning Classification Algorithm with Enhancements. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=OneR.
Holte, Robert C. 1993. “Very Simple Classification Rules Perform Well on Most Commonly Used Datasets.” Machine Learning 11 (1): 63–90. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022631118932.